If you have recently connected to certain Wi-Fi Network and you can’t remember which password you did used for that connection, I will show you which steps you need to perform in your Mac OS X and see which password you need to use. To turn Wi-Fi off and on again click on the Wi-Fi logo in the menu at the top right of your Mac and select Turn Wi-Fi Off. Disconnect Bluetooth Try disconnecting Bluetooth. Using WiFi Thief Detector - Detect Who Use My WiFi, in seconds you know how many and which devices is connected to your wifi router with IP, MAC ID and vendor listing. WiFi Thief Detector - Detect Who Use My WiFi always find all connected devices on my wifi router and Check who is using my wifi!
There could be multiple reasons for Mac not connecting to WiFi network. You will find below a number of methods to fix WiFi connectivity problems on Mac.
Mac Not Connecting to WiFi
The problem of Mac Not Connecting to WiFi Network could be due to a variety of reasons, ranging from glitches in Modem/Router, over crowded DNS servers to other network connectivity issues.
In many cases, the problem of WiFi and Ethernet not working on Mac ends up being due to loose or disconnected cable connections.
Hence, rule out this issue by inspecting the cable connections, before proceeding with other methods to fix this problem.
1. Power Cycle Modem/Router
Before going ahead with more complex troubleshooting steps, try this simple troubleshooting fix.
1. Disconnect the Modem/Router from Power Supply. You can either pull out the power cable from the Wall Socket or use the ON/OFF switch (If available).
2. Wait for 60 seconds and connect the Modem/Router back to its power supply.
2. Reboot Your Mac
Simply, restart the MacBook and you might be surprised to see it connecting to WiFi Network.
1. Completely Shut Down your Mac
2. Wait for 60 seconds and restart your device.
3. After Mac Restarts, see if you are now able to connect to WiFi.
3. Forget WiFi Network
Making the Mac forget its WiFi Network and then rejoining the WiFi Network is known to fix this issue.
1. Click on the Apple Logo in top-menu bar and select System Preferences… in the drop-down menu.
2. On System Preferences screen, click on the Network option.
3. On the Network screen, select WiFi Network in left menu bar and click on the Advanced button.
4. On the next screen, select the WiFi Network that you want to forget and click on the minus (-) sign.
5. Click on OK to save this setting and close the Network screen.
6. Next, click on the WiFi Icon located at top right corner of your screen and select your WiFi Network in the drop-down menu.
7. When prompted, enter your WiFi Network Password.
WiFi should now be working on your Mac
4. Renew DHCP Lease
In case your Mac appears to be connected to WiFi Network, but you are unable to connect to Internet, you may need to Renew DHCP Lease.
1. Click on Apple Logo in the top menu-bar > select System Preferences… in the drop-down menu.
2. On System Preferences screen, click on the Network option.
3. On the Network screen, click on WiFi in the side-menu and click on the Advanced button.
4. On the next screen, click on TCP/IP tab and click on Renew DHCP Lease button.
5. Click on OK to save the revised settings.
5. Disconnect Bluetooth
Sometimes Bluetooth can interfere with WiFi Network and some users have reported being able to connect to WiFi Network after disabling Bluetooth on their Mac.
1. Click on the Bluetooth Icon located at top right corner of your screen and click on Turn Bluetooth OFF option in the Drop-down menu.
2. Restart Mac and see if you are now able to connect to WiFi.
6. Change DNS Servers
If you are frequently experiencing WiFi connectivity problems on your Mac, the issue might be related to DNS server of your Internet Service Provider (ISP) being crowded.
In such a case, switching to Google DNS or DNS Servers provided by Amazon or OpenDNS might help in fixing the issue.
Free DNS servers as provided by Google, Amazon and OpenDNS are reliable and likely to be much faster than DNS Servers used by your Internet Service Provider.
As the number of Wi-Fi networks rapidly explodes, detecting, managing, and maintaining your Wi-Fi can become problematic. When everyone around you is blasting their own Wi-Fi signals—particularly if in large apartment buildings or business complexes with lots of other large companies—you’re more likely to experience problems with Wi-Fi signals dropping out, poor connectivity, and slow performance.
Even within your own Wi-Fi network, several optimizations could help ensure your network is functioning appropriately, including router placement, appropriate channel, and security measures. And of course, analyzing and understanding your wireless network is key.
One of my favorite tools for discovering and solving these problems is SolarWinds® Network Performance Monitor (NPM). It includes high-performance network monitoring and insights and troubleshooting features to ensure your network starts working again as soon as possible after a problem arises. In particular, the SolarWinds heat map feature allows you to see where Wi-Fi signal is strong, and “dead zones” with low connectivity.
What Does a Wi-Fi Analyzer Do?
Most Wi-Fi network analyzers work in a similar way, in which you can choose a wireless spectrum to examine, such as 2.4GHz or 5GHz. The analyzer then examines that spectrum to view networks, their channels, and signal strength.
In simple terms, a Wi-Fi analyzer gathers information about access points and channels on your network and displays it in an easy-to-understand, visually accessible way. A wireless network analyzer can help you maintain connection quality, which can be vital for numerous business needs and performance metrics. Wi-Fi signals are constantly changing, and small changes in the network can have massive effects on the overall connection uptime.
Using a Wi-Fi network analyzer can collect data and help you identify problems, or it can indicate potential solutions such as switching to another channel to reduce congestion. You can also use this type of tool to discover areas in your facility with a weak Wi-Fi signal.
Best Wi-Fi Network Analyzer Software in 2020
In my opinion, using Wi-Fi analyzer software can be an excellent tool for optimizing business and even at-home Wi-Fi performance. This kind of software is usually easy-to-use and can provide great benefits in terms of connection reliability, signal strength, and download speeds.
Network Performance Monitor
Of the different tools available on the market, the SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor, with its Wi-Fi analyzer, is the most comprehensive. Despite its extensive list of features, it remains simple for both beginner and advanced users.
The relevant feature here is the heatmapping capability allowing you to create multiple color-coded maps of your facilities using real device data to display signal strength. You can automatically update these maps for a real-time understanding of your wireless network. Having at-a-glance insights into your Wi-Fi can really help with troubleshooting (especially when end users come knocking with complaints about connectivity).
Beyond heatmapping, NPM offers a range of useful network management features. For instance, its proprietary NetPath™ tool lets you detect and display network pathways with a visual traceroute. This allows you to simply determine where slowdowns and issues exist, as you can see the performance and information between individual nodes. Furthermore, with the PerfStack™ feature, you can compare the performance of different metrics side-by-side, so you can correlate multiple types of data across a common timeline.
Overall, SolarWinds NPM has an impressive suite of tools, and each has clean and beautiful visualizations and displays. Furthermore, NPM scales well and includes the ability to hook in with the SolarWinds High Availability platform, to ensure even fewer network drops, with strong failover protection.
NetSpot
NetSpot has a beautiful, easy-to-use interface, and is suitable for both beginners and experienced network administrators. It uses two different modes: discovery mode and survey mode. The first mode looks at a snapshot of the Wi-Fi networks near you, while survey mode can provide more detailed heat maps of Wi-Fi strength.
NetSpot is easy to install and includes several other visual representations of the wireless spectrum and the data it can collect. There are four different versions: free, home, commercial, and enterprise. The difference between them is the number of zones you can look at, how many access points you can scan, and the number of data points you can collect with a scan.
InSSIDer
Another product to consider is InSSIDer. This established Wi-Fi analyzer tool for Windows is very reliable. The InSSIDer tool is generally intended for enterprise and business use, rather than for home users. Despite being geared toward admins, it’s still relatively easy to use.
It gathers the data you would expect: channel, signal strength, MAC addresses, and encryption type for each access point on the network. InSSIDer then provides you with a “link score” for each connection. The higher the score, the better. The software is easy to install, with comprehensive guides and links to free webinars if you need more assistance.
NetCut
Consider NetCut if you’re looking for a solution for professional or enterprise use. It was originally created to be a back-end solution, but it can be used by anyone for network investigating and debugging.
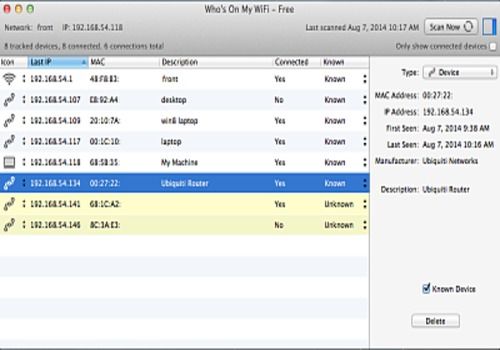
NetCut allows you to monitor LAN activity and can display all the IP and MAC addresses and data of devices that are connected or have ever connected to your network.
With NetCut, you can kick someone off your network or restore their access at will. The main issue with NetCut for beginner users is that it has a lot of machine-translated documentation that may be hard to understand for someone who is not a network administrator, and a slightly more complex interface.
NetCut includes an extra layer of protection called NetCut Defender, which protects your computer from ARP and MAC address spoofing.
WiFi Analyzer
Unlike NetSpot and NetCut, WiFi Analyzer is intended primarily for home or temporary use. It is an app for Windows 10, available on the Microsoft Store. It comes in basic and pro versions, and the basic version includes everything you need to analyze your Wi-Fi network. The app takes your network and turns the data into easy-to-understand visualizations, suggesting which channel you should use to reduce congestion.
For someone new to Wi-Fi analyzer tools, this would be a potential choice. For enterprise needs or larger networks, it’s probably much too limited.
Vistumbler
Like most other Wi-Fi analyzers, Vistumbler scans nearby networks for access points and can map your Wi-Fi network and connectivity strength while showing you detailed information about each network. It provides network status, MAC address, SSID, signal strength, channel number, and network type.
Vistumbler is set apart by its GPS support, which can integrate with Google Earth to display Wi-Fi networks. This feature is for people who may be driving, walking, or cycling around to try to find Wi-Fi networks to use. When Vistumbler discovers a Wi-Fi network with this feature, the app can show you where the network is on a map and other network information.
The main downside is that Vistumbler is not easy to use, and the user interface can be difficult to navigate. Again, it’s not a full enterprise solution for Wi-Fi analysis.
WiFi Commander
With good-looking graphics and sophisticated UI, WiFi Commander is one of the more attractive Wi-Fi analyzer tools. You can scan and filter nearby Wi-Fi networks and create 3-D graphs of the results. If your laptop has touchscreen capabilities, you can use touch to move and interact with the 3-D visualization.
The WiFi Commander app shows Wi-Fi signal strength and displays it in real-time so you can use the most recent data to join the strongest or most stable Wi-Fi network.
Wireshark
If you need a free or open-source Wi-Fi analyzer tool, check out Wireshark. Its purpose is to analyze and troubleshoot different communications protocols, and it includes the ability to look at Wi-Fi. Wireshark is very complicated to use, and you’ll need some training to use it. As such, it’s normally only used by networking and Wi-Fi professionals. In addition, there are obvious disadvantages for relying on open-source tools for business use, so you may want something with a bit more built-up functionality.
If you’re looking for something a little more basic when it comes to Wireshark, SolarWinds has a free tool called Response Time Viewer for Wireshark designed to help you analyze packet capture files as well as visualize response time in Wireshark.
Who Is On My Wifi Mac Download Mac
Wi-Fi Analysis Solutions
In general, there’s no shortage of tools and software to help you monitor and organize your Wi-Fi networks, whether you’re a casual user or an enterprise professional. With the inclusion of high-reward tools such as heatmaps, visualizations, and performance metric graphs, the best Wi-Fi analysis tools and network management tools can revolutionize how you get the most out of your connection.
Who's On My Wifi Download
I recommend SolarWinds NPM due to its more robust suite of offerings and simple learning curve for new users. It’s much more robust than some of the limited-scope tools I mentioned above. Even so, I find the SolarWinds platform both intuitive and efficient.
Related Reading
Who Is On My Wifi Mac Downloads
How to Tame—and Redefine—Your Network Now – If you’re interested in considering how networks are changing and evolving, as well as the ways in which you may need to adapt your network management, read this article on how to prepare for tomorrow’s network topography.